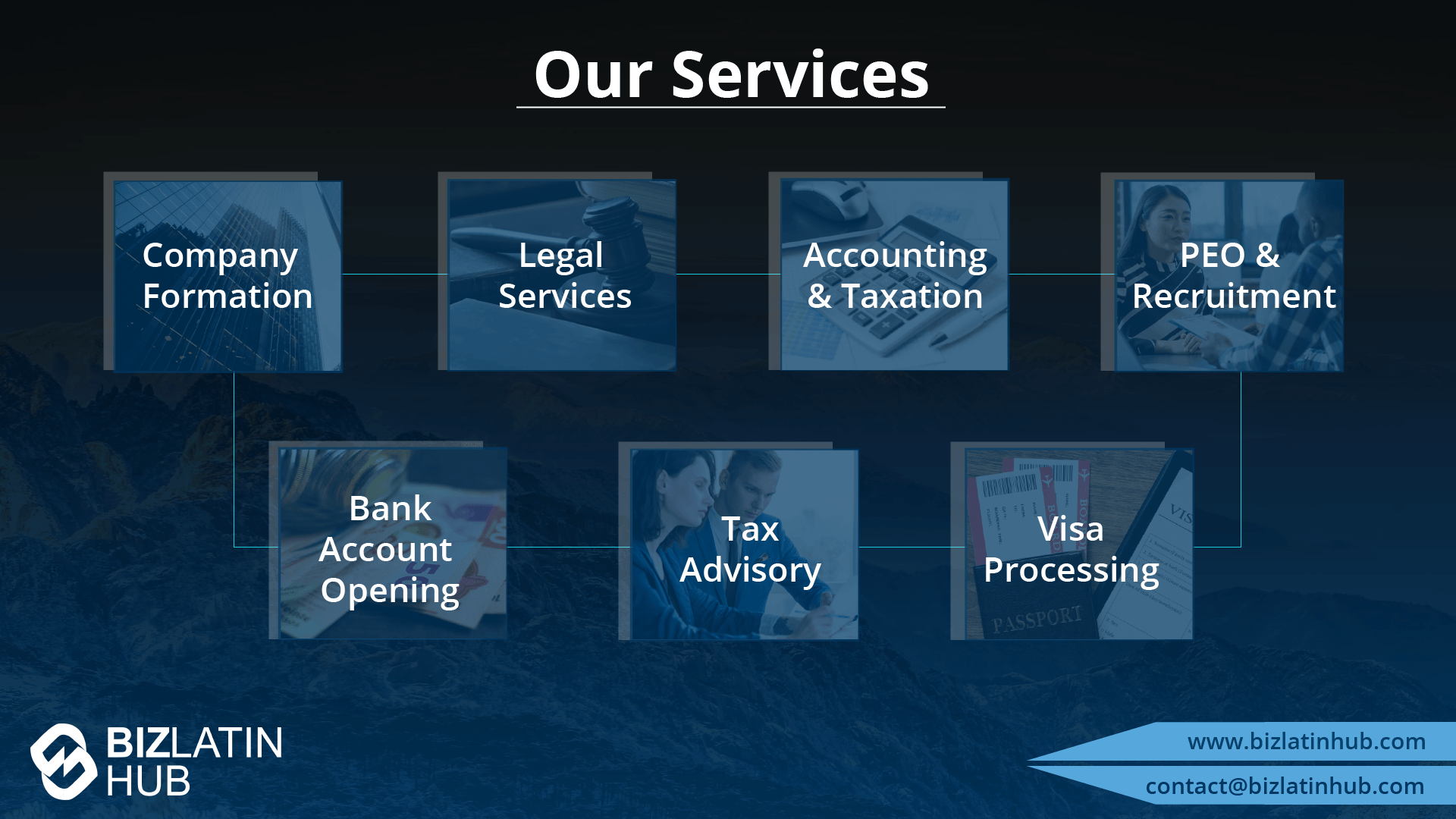
Starting a business in Barbados means entering a dynamic business environment. Employers find it attractive for its skilled workforce. Understanding Barbados’ labor laws is important. It helps employers meet legal duties. It also supports good employee relationships. This guide explains key parts of Barbados’ labor laws. It offers information for employers on employment terms, worker rights, and hiring methods.
Key Takeaways: Barbados Labour Law
| What is the Employment Rights Act 2012? | This is the main labor law. It protects employee rights. It details termination conditions, notice, and severance pay. |
| Are oral contracts legal? | Employers must provide a written statement of employment particulars. |
| What are the main statutory contributions an employer must make? | It is mandatory for employers to make monthly contributions to the NIS for each employee. |
| Is it easy to terminate an employee in Barbados? | There are strict rules governing unfair dismissal. |
| What is the national minimum wage in Barbados? | As of April 2021, the national minimum wage in Barbados is BBD$8.50 (USD$4.25) per hour. |
Key Obligations Under the Employment Rights Act
Barbados has a detailed legal system for labor relations. Key laws define employment rights, contracts, and termination rules. Employers and employees should know these laws. This knowledge ensures a fair work environment.
1. Provide a Written Statement of Particulars
Employers must give every employee a written document outlining the key terms of their employment, including job title, pay rate, working hours, and holiday entitlement.
Expert Tip: The Critical Importance of the Written Statement
Based on our experience, the requirement to provide a written statement of particulars is a frequent point of non-compliance for new employers. The Employment Rights Act is very strict on this point: this document, which functions as the official employment contract, must be given to the employee at the start of their employment.
Failure to do so can weaken the employer’s position significantly in any future dispute. We advise all clients to have a compliant template ready and to make providing this document on the first day of work a non-negotiable part of their onboarding process.
2. Comply with Wage and Working Time Rules
All employers must pay at least the national minimum wage. Overtime pay is required for work exceeding the standard 40-hour work week.
3. Make National Insurance Scheme (NIS) Contributions
It is mandatory for employers to make monthly contributions to the NIS for each employee. This provides employees with access to a range of social security benefits.
4. Follow Fair Termination Procedures
An employer must have a fair and legally valid reason for terminating an employee. They must also follow a fair procedure, including providing the required notice period and severance pay where applicable.
| Law/Scheme | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Employment Rights Act 2012 | This is the main labor law. It protects employee rights. It details termination conditions, notice, and severance pay. |
| National Insurance Scheme | This scheme gives financial help for sickness, maternity, and other situations. |
| Bajan Holidays with Pay Act | This act guarantees paid leave for workers after one year of employment. |
| Barbados Labour Department Act | This act describes duties for labor regulation. It ensures fair work practices. |
| Occupational Training Act | This act provides training programs for different job roles. It helps improve worker skills. |
| National Insurance and Social Security Act | This act supports worker welfare. It provides for maternity, sickness, and old-age pensions. |
These laws help create a balanced relationship between employers and employees.
Employment Terms and Contracts
Employment contracts in Barbados must have clear terms. Contracts should detail job duties, work hours, pay, and benefits. Clear terms help both employers and employees agree. Contract types include permanent and fixed-term. Permanent contracts are for ongoing work. Fixed-term contracts have set start and end dates. An employer must give written notice if they will not renew a fixed-term contract. The Employment Rights Act allows either party to end a contract with notice. The notice period depends on the employee’s length of service. Senior positions might have different terms for overtime pay.
Employee Rights and Protections
The Employment Rights Act 2012 is the main protector of employee rights in Barbados. This law specifies worker rights and related matters. The law sets maximum lengths for probationary periods. Employers must use fair procedures when dismissing employees on probation. Casual workers in Barbados also have rights. These rights include minimum wage and safety standards, even with varied work hours. Barbados’ labor laws also cover industrial relations and workplace safety. These laws follow standards from the International Labour Organization.
Termination and Probation Rules
The Employment Rights Act specifies termination procedures. Notice periods change based on pay frequency and job tenure. Valid reasons for dismissal include poor performance, misconduct, or redundancy. Employers must give written notice and a clear reason for termination. This helps avoid claims of unfair dismissal. Probation periods do not have fixed legal limits. They often start at three months, following company policy. Disputes about employment rights can go to the Chief Labour Officer. If not resolved, the Employment Rights Tribunal may hear the case.
Leave Entitlements: Maternity, Sick Leave, and Public Holidays
In Barbados, employees with over 12 months of service receive 12 weeks of paid maternity leave. This leave includes six weeks before and six weeks after childbirth. A doctor can recommend extensions for health reasons. An employee can take maternity leave up to three times with the same employer. Employers can ask for a doctor’s note if sick leave exceeds two days. The National Insurance Scheme pays for sick and maternity leave. For maternity, it pays 100% of the average insurable earnings. This offers financial support during leave.
Understanding Workforce Demographics
Barbados is a small Caribbean island. Its workforce demographics result from historical, social, and cultural influences. Economic conditions also shape these traits. Employers in Barbados should understand the labor market’s specific features. Different rules and cultural factors affect employment choices.
Barbadian labor laws set clear rights and duties. The Employment Rights Act 2012 protects workers. This law affects the workforce’s makeup and behavior. Knowing these laws is vital for employers and employees.
Workforce Demographics in Barbados:
- Gender: Women are a significant part of the workforce.
- Duration: Continuous employment influences rights and benefits.
- Hours: Standard work hours vary by industry.
Employers should note these points when hiring:
- Contracts: Various employment contract types exist.
- Regulations: Comply with visa and legal rules.
- Hours: Standard and overtime hours are regulated.
Understanding these points helps employers operate smoothly. It also ensures they follow Barbadian laws. This creates a good employment relationship for everyone.
The Role of the National Insurance Scheme (NIS)
The National Insurance Scheme (NIS) is the social security system in Barbados. It is a compulsory, contribution-based fund that provides a range of benefits to employees, including sickness, maternity, injury, and pension benefits. All employers must register with the NIS and make monthly contributions for their employees.
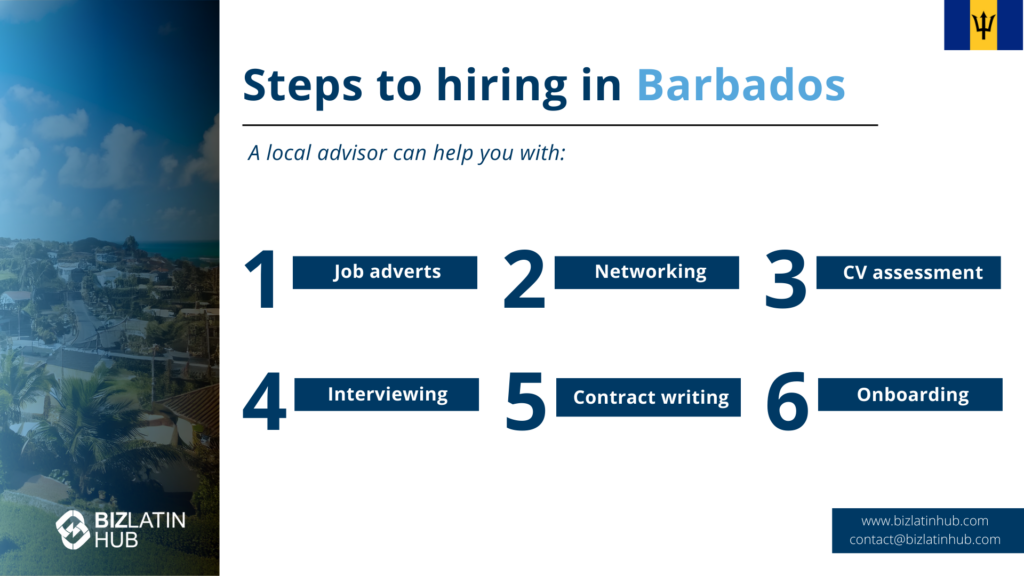
Recruitment Practices in Barbados
Barbados uses traditional interview methods. It also values interpersonal skills, qualifications, and cultural fit. Job candidates should research the employer. They should understand company values and job needs.
Popular Recruitment Platforms:
- LinkedIn
- Caribbean Jobs
Companies use these platforms to find talent globally. Specialized recruitment agencies can also help companies create good recruitment plans.
Key Points for Job Seekers:
- Research the company.
- Understand job details.
- Match company values.
Barbados’ economy has a strong tourism focus. This makes it a key place for recruitment. This increasing demand means companies need structured interviews. They must select candidates who meet professional and cultural standards.
Hiring Practices and Considerations
Employers in Barbados must follow the Employment Rights Act 2012. This law protects employee rights. It includes rules for termination notices and severance pay.
Fixed-term Employment Contracts:
- Require written notice for non-renewal.
- May involve severance pay.
Temporary Employment Contracts:
- Are suitable for short-term or seasonal jobs.
- Are useful when businesses need extra staff.
Companies must keep accurate records of work hours, including overtime. This ensures they follow labor laws and avoid penalties. Not doing so can lead to fines or legal problems.
The national minimum wage in Barbados is 8.50 Barbadian Dollars per hour (as of April 2021). This is the lowest pay rate employers can offer.
Key Points to Remember:
- Choose the right contract type for your needs.
- Follow the Employment Rights Act.
- Keep detailed records of work hours.
- Pay at least the minimum wage.
Following these practices helps employers build fair and legal employment relationships.

Employer of Record (EOR) Services
In Barbados, an Employer of Record (EOR) is very helpful for businesses. An EOR allows companies to hire global employees without setting up a local office. EORs are third-party groups. They handle important tasks like payroll, taxes, benefits, work visas, and following labor laws.
Using EOR services helps companies operate well in Barbados. Businesses can focus on their main work while the EOR manages administrative tasks. EORs also ensure companies follow local rules. This allows for smooth international growth.
Companies should check their EOR agreements regularly. This makes sure the partnership meets their goals and adapts to business changes.
Benefits of Using EOR Services
Using an Employer of Record (EOR) gives big advantages to businesses growing in Barbados. EORs manage key HR tasks like payroll, tax filing, and benefits. This makes operations simpler. It also ensures companies follow local employment laws. An EOR acts as a link between a business and its workers. This keeps operations running smoothly. EORs stay current with Barbados labor laws to ensure full compliance. Working with an EOR leads to effective employment management. Regular communication helps companies handle workforce changes well. So, businesses can focus on their main operations. The EOR handles the legal details.
Full-Time and Contractor Employment Differences
Businesses in Barbados need to know the difference between full-time and contractor roles. Employment contracts for these roles are usually Permanent or Fixed-Term. Both are legally accepted. Full-time employees get benefits like health insurance and paid time off. Contractors do not get these benefits. Contractors can work on many projects for different companies. This makes them self-employed. Problems can arise when telling international contractors apart from full-time staff. Hiring contractors can seem cheaper because they do not get benefits. Companies must make sure their employment contracts follow the Employment Rights Act 2012. This protects employee rights and follows Barbadian labor laws.
Compensation and Benefits Management
In Barbados, employers can create custom employee benefits within certain rules. The Employment Rights Act 2012 gives a legal structure. It protects employee rights and sets job standards. Employers can offer holiday bonuses and extra vacation days. This can increase employee happiness. Companies must pay into a social security fund. They do this by registering with the National Insurance director. This payment protects employees from various risks. Payroll uses a Pay As You Earn (PAYE) system. Taxes are taken from wages regularly. Generous vacation and leave policies are common. This shows the country’s focus on work-life balance.
Minimum Wage and Overtime Rules
Barbados has clear rules for minimum wage and overtime. The minimum wage is between BDS6.25andBDS8.50 per hour. This depends on employment terms. For workers not paid weekly or daily, the minimum is BDS8.50perhour.A40−hourworkweekmeansaminimumweeklywageofBDS340.00. Employees working an 8-hour day without weekly terms earn at least BDS$68.00. Standard work hours are a 40-hour week over five days. Each day is 8 hours long. Overtime pay is 1.5 times the regular rate for hours worked past the standard workweek.
Managing Employee Benefits
In Barbados, labor laws let employers design employee benefits with some freedom. This includes holiday bonuses and extra vacation days. These can be more than what the law requires. Retirement benefits are also a standard part of pay. Both employer and employee must contribute. Companies often have generous leave policies. These include annual leave, sick leave, and public holidays. This promotes work-life balance. Sick leave policies in Barbados require a doctor’s note after two days of absence. The National Insurance Scheme pays sick pay after three days if the employee has contributed. On public holidays, employees who work get double pay, as per local labor laws.
Government Initiatives Supporting Employers
The Barbados government has several programs to help employers. The Barbados Labour Department Act defines duties for labor regulation. It ensures fair practices. The Occupational Training Act creates training programs for various job roles. This improves workforce skills.
Employers gain from the Employment Rights Act 2012. This act states employee rights. It provides clarity in employment relationships. The National Insurance and Social Security Act helps employee welfare. It offers maternity, sickness, and old-age pensions.
Barbados follows international labor standards. It has approved many ILO Conventions. These focus on industrial relations and job safety. This approach provides a clear system for labor standards. It benefits both employers and employees.
Key Employer Support Initiatives:
- Barbados Labour Department Act: Regulates labor practices.
- Occupational Training Act: Provides training programs.
- Employment Rights Act 2012: Clarifies employee rights.
- National Insurance and Social Security Act: Offers financial benefits.
- ILO Conventions: Ensure international labor standards.
These programs help create a fair work environment. They assist employers in meeting legal duties while promoting safe workplaces.
Differences: Employer of Record (EOR) vs. Professional Employer Organization (PEO)
An Employer of Record (EOR) and a Professional Employer Organization (PEO) have different roles in managing employment. An EOR becomes the legal employer of a workforce.
It handles payroll, taxes, benefits, and compliance. It does this without the business needing a local office. This legal status lets businesses hire globally without opening a base in each country.
A PEO, however, co-employs workers. It shares duties for payroll and HR tasks with a client that has a local office. The need for a local office is a main difference between an EOR and a PEO.
Here’s a table showing the differences:
| Feature | Employer of Record (EOR) | Professional Employer Organization (PEO) |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Employer | Yes | No (co-employment) |
| Local Entity Needed | No | Yes |
| Global Employment without Presence | Yes | No |
Key Points:
- EOR handles all employment tasks alone.
- PEO needs shared duties with a local partner.
- EOR gives a simpler, complete solution.
The choice between an EOR and a PEO depends on business needs and local laws.
Incorporation and Work Permits in Barbados
In Barbados, foreign nationals need a work permit to get a job. The process requires a valid job offer from a local employer. There are two main types of work permits:
- Short-term work permit: Lasts up to 11 months.
- Long-term work permit: Lasts up to three years.
The employer or sponsor usually applies for the work permit. The applicant needs a valid passport. The passport must be valid for at least six months beyond their planned stay in Barbados. Getting a work permit without a job offer is very hard. This is because employment sponsorship is needed.
Here’s a quick summary:
| Work Permit Type | Duration | Applicant Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Short-term | Up to 11 months | Passport validity + Job offer |
| Long-term | Up to three years | Passport validity + Job offer |
Employers should make sure all immigration steps are followed. This helps the process go smoothly for both the employer and the employee. Knowing these steps makes getting a work permit in Barbados easier.
Compliance and Regulatory Obligations
In Barbados, the Employment Rights Act 2012 provides the main rules for employment. Employers must follow this act to protect employee rights. It includes rules for industrial relations, safety, health, and labor standards. These rules ensure a safe and fair work environment.
Employers and employees must give notice before ending a job contract. This is a legal rule. If a fixed-term contract is not renewed, the employer must give written notice. This ensures fair treatment.
The National Insurance Scheme (NIS) gives sick pay after three days of absence. Employees must pay into this fund to get the benefit. Employers must handle this as part of payroll.
Here is a brief summary of some key points:
| Key Areas | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Notice Period | Notice is needed before ending employment. |
| Fixed-Term Contracts | Written notice is required for non-renewal. |
| Sick Pay | Available through NIS after three days of absence, if paid into. |
These legal rules create an orderly employment system.
Cultural Nuances in the Barbadian Workplace
Understanding cultural points in the Barbadian workplace is key to a good work atmosphere. Barbados has a rich cultural background. This background affects work habits, communication, and social interactions.
Key Cultural Aspects
- Respect for Hierarchy: Barbadians often respect formal structures. It is important to show respect to senior staff and managers.
- Polite Communication: Barbadians usually use polite and formal words in professional places. Greetings like “Good morning” or “Good afternoon” are usual.
- Punctuality: Though it can differ, being on time is valued. Arriving on time shows professionalism.
- Community and Teamwork: There is a strong community feeling. Teamwork and working together are highly valued.
- Work-Life Balance: Barbadians generally value their free time. Keeping work and personal life separate is important.
Table: Common Workplace Etiquette
| Aspect | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Greetings | Polite and formal |
| Meeting Etiquette | Punctuality is valued. |
| Decision Making | Respect formal structures. |
| Communication Style | Polite and friendly. |
| Team Interaction | Focuses on working together and community spirit. |
Knowing these cultural traits helps build good workplace relationships in Barbados.
Conclusion and Best Practices for Employers
Employers in Barbados should focus on following labor laws. This maintains fair working conditions. These laws include the Employment Rights Act 2012. This Act protects employee rights and ensures equality.
Good practices for employers include:
- Create clear employment contracts. These should state the minimum wage, working hours, and termination rules.
- Make sure sick leave policies require a doctor’s note after two days. Policies should match the National Insurance Scheme for sick pay.
- Adjust employment contracts to include terms like specific sick leave and holiday bonuses.
Employers should stay aware of international standards. Barbados labor laws reflect International Labour Organization (ILO) Conventions on safety and labor standards. This practice ensures global compliance and local fairness.
In summary, understanding and following labor laws helps employers create a fair work environment. This method protects employee rights and ensures legal business operations. Changing policies to match local laws and international guides is vital for success.
Barbados’ Economic Scene
Barbados has a varied economy. Tourism, financial services, and agriculture are its main supports. The island’s beautiful beaches and lively culture attract many visitors.
Tourism provides the most income. Visitors often come from North America and Europe. They enjoy the island’s warm weather and friendly people.

Financial services are another important area. Barbados has a solid legal system. It provides offshore banking and insurance services. These services attract global businesses.
Agriculture also adds to the economy. Sugarcane is a primary crop. Rum production is also notable. Barbados exports these goods globally.
Key facts about Barbados’ economy:
- Main Sectors: Tourism, financial services, agriculture
- Major Income Source: Tourism
- Key Exports: Sugar, rum
- Primary Partners: North America, Europe
Barbados also has economic challenges. The country needs to manage its high national debt. Efforts to diversify the economy are ongoing. Sustainable development is also a growing focus.
In short, Barbados presents a mixed economic picture. It has opportunities and challenges. The nation aims to balance economic growth with sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions: Barbados Labour Law
What are the key labor laws in Barbados?
The main labor laws in Barbados include the Employment Rights Act 2012, the National Insurance Scheme, the Holidays with Pay Act, the Barbados Labour Department Act, the Occupational Training Act, and the National Insurance and Social Security Act. These laws cover employee rights, benefits, fair work practices, and training programs.
What is the national minimum wage?
As of April 2021, the national minimum wage in Barbados is BBD $8.50 per hour.
What are the leave entitlements in Barbados?
Employees in Barbados are entitled to 12 weeks of paid maternity leave after one year of service, with six weeks before and six after childbirth. Sick leave requires a doctor’s note after two days. Public holidays are paid, and employees working on those days must be paid double.
What are the standard working hours?
The standard work week in Barbados is 40 hours, typically configured as eight hours per day over five days. Work performed beyond these hours is generally considered overtime.
What constitutes unfair dismissal?
Unfair dismissal occurs when an employer terminates an employee without a valid reason (such as misconduct, poor performance, or redundancy) or fails to follow a fair termination procedure. An employee with at least one year of service can file a claim with the Employment Rights Tribunal.
How are NIS contributions calculated?
NIS contributions are calculated as a percentage of the employee’s insurable earnings, up to a certain maximum. The employer and the employee both contribute a portion. The employer is responsible for deducting the employee’s share and remitting the total amount to the NIS office monthly.
The National Insurance Scheme (NIS) in Barbados provides financial support for maternity leave, sickness, and old-age pensions. Employers and employees contribute to the fund. Benefits like sick pay begin after three days of absence, and maternity benefits cover up to 100% of insurable earnings.
Biz Latin Hub can help you with labor law in Barbados
At Biz Latin Hub, our multilingual team of company formation specialists has extensive experience in supporting foreign executives when starting a business in Latin America. We offer a complete set of services for your business needs, such as legal, accounting, and recruitment support.
You can rely on us as your main contact for entering and doing business in any of the 18 markets in Latin America and the Caribbean where we operate.
Contact us now for personalized assistance or a free quote on company formation in Latin America.
Learn more about our team and expert authors.